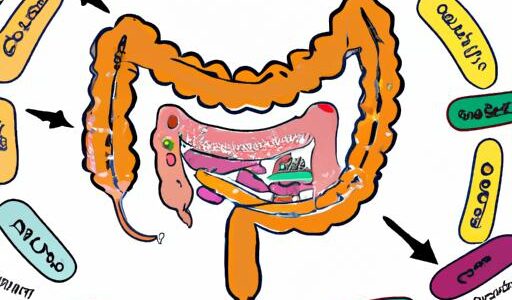
Do you ever wonder how long it takes for the food you consume to be fully digested? Understanding the digestion process is not only fascinating but also crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of digestion, exploring the factors that influence digestion time and providing valuable tips for promoting a smooth digestive system.
Digestion is a remarkable journey that our food embarks on once it enters our body. It undergoes a series of complex processes to extract essential nutrients and eliminate waste. Picture your digestive system as a well-coordinated team of organs, enzymes, and muscles working harmoniously to break down the food you consume.
The process begins as soon as you take a bite. Chewing helps to mechanically break down the food, while saliva begins the chemical breakdown with the help of enzymes. Once swallowed, the food travels down the esophagus and enters the stomach, where it is further broken down by stomach acids and enzymes. From there, it moves into the small intestine, where most of the nutrient absorption takes place. Finally, the remaining waste material reaches the large intestine, where water is absorbed, and stool formation occurs before elimination.
Understanding the digestion process is not only fascinating but also essential for optimizing our overall health. By knowing how long it takes for food to be digested, we can make informed choices about our diet and lifestyle. Stay tuned as we explore the factors that influence digestion time and discover some surprising insights along the way.
Now that we have laid the groundwork, let’s dive deeper into the factors that influence digestion time and unravel the mystery of how long it takes for our bodies to digest food.
Digestion Process
Have you ever wondered what happens to your food once it enters your body? The digestion process is a fascinating journey that our food undertakes, traversing through various stages in the digestive system. Let’s take a closer look at how this extraordinary process unfolds.
A. Explanation of the Journey of Food through the Digestive System
Once you take a bite of food, it embarks on a remarkable journey through your digestive system. It all starts in the mouth, where the mechanical breakdown of food begins through chewing. Enzymes in your saliva also initiate the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates.
From the mouth, the food then travels down the esophagus, a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Peristalsis, a wave-like muscle contraction, propels the food downward, ensuring it reaches the stomach.
In the stomach, the food encounters a highly acidic environment. Stomach acids and enzymes, such as pepsin, work together to break down proteins into smaller fragments. This process helps prepare the food for further digestion in the small intestine.
As the partially digested food leaves the stomach, it enters the small intestine, where the majority of nutrient absorption occurs. Here, various enzymes and bile from the liver and gallbladder further break down the food into its nutrient components. These nutrients are then absorbed through the intestinal lining and transported to other parts of the body via the bloodstream.
The remaining undigested material, now referred to as waste or stool, moves into the large intestine. In the large intestine, water is absorbed from the waste, making it more solid. The colon, part of the large intestine, plays a crucial role in the formation of feces. Finally, the waste is eliminated from the body through a bowel movement.
B. Role of Digestive Enzymes and Their Importance
Digestive enzymes are essential players in the digestion process. These specialized proteins help break down complex food molecules into smaller, more manageable forms that can be easily absorbed by the body. Each type of enzyme has a specific role in breaking down different nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
For example, amylase is an enzyme that helps break down carbohydrates into simple sugars, while proteases assist in breaking down proteins into amino acids. Lipases, on the other hand, play a crucial role in breaking down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Without these digestive enzymes, our bodies would struggle to extract the necessary nutrients from the food we consume. They are key players in ensuring efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
C. Breakdown of the Different Stages of Digestion
The digestion process can be broadly categorized into several stages. Each stage plays a pivotal role in breaking down food and facilitating nutrient absorption. Let’s explore these stages:
-
Ingestion: This is the process of taking food into the mouth and beginning the mechanical breakdown through chewing.
-
Mechanical Digestion: Chewing and the muscle contractions of the stomach and intestines help mechanically break down food into smaller particles, increasing its surface area for better enzyme action.
-
Chemical Digestion: Enzymes, acids, and bile break down complex food molecules into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the body.
-
Absorption: Nutrients are absorbed through the walls of the small intestine and transported to the bloodstream for distribution to cells throughout the body.
-
Elimination: The indigestible waste material is formed into feces in the large intestine and eliminated from the body through bowel movements.
Understanding the journey of food through the digestive system, the role of digestive enzymes, and the breakdown of the different stages of digestion is crucial in comprehending the time it takes for our bodies to digest food. In the next section, we will explore the various factors that can influence digestion time.
Factors Influencing Digestion Time
When it comes to digestion time, several factors come into play. Understanding these factors can shed light on why digestion time varies from person to person. Let’s explore the main influencers:
A. Type of Food Consumed
The type of food you consume plays a significant role in determining how long it takes to be digested. Some foods are easier to break down and move through the digestive system quickly, while others require more time and effort. For example, simple carbohydrates like refined sugars are typically digested faster compared to complex carbohydrates and proteins. Fatty foods also tend to take longer to digest as they require the release of bile for proper breakdown. So, the composition of your meals can directly impact digestion time.
B. Individual Metabolism and Health Factors
Each person’s metabolism is unique, and this directly affects digestion time. Metabolism refers to the rate at which your body converts food into energy. Individuals with a faster metabolism may experience quicker digestion compared to those with a slower metabolism. Additionally, certain health factors can influence digestion time. Digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or conditions like gastroparesis can significantly slow down the digestion process.
C. Impact of Fiber, Fat, and Protein on Digestion Time
The presence of fiber, fat, and protein in your meals can influence digestion time. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, add bulk to your stool and promote regular bowel movements. They can speed up digestion and prevent constipation. On the other hand, high-fat foods take longer to break down as they require more effort from the digestive system. Protein-rich foods, like lean meats and legumes, also tend to take longer to digest compared to carbohydrates.
Understanding how these factors influence digestion time allows us to make informed choices about our diet and lifestyle. In the next section, we will explore the average digestion times for different foods, providing you with a clearer picture of what to expect.
Average Digestion Times for Different Foods
When it comes to digestion, not all foods are created equal. Different food groups have varying digestion times, which can impact our overall well-being. Let’s take a closer look at the average digestion times for various food groups and explore the factors that influence how quickly or slowly our bodies break them down.
A. Overview of Digestion Times for Common Food Groups
-
Fruits and Vegetables: These fiber-rich foods are generally easier to digest and pass through the digestive system relatively quickly. On average, fruits and vegetables take around 20 to 30 minutes to leave the stomach and move into the small intestine for further processing.
-
Proteins: Foods rich in protein, such as meat, fish, and poultry, require more time to digest due to their complex structure. It takes approximately 2 to 4 hours for proteins to be broken down into amino acids and absorbed by the body.
-
Carbohydrates: Foods like bread, pasta, and rice fall into this category. Carbohydrates are usually digested quickly, with digestion starting in the mouth and continuing in the stomach and small intestine. The process typically takes around 2 to 3 hours.
-
Fats: Fatty foods, like oils, butter, and cheese, tend to be digested slowly. The digestion of fats begins in the stomach and can take up to 4 to 5 hours to complete.
B. Specific Examples of Food Digestion Times
While the digestion times mentioned above provide a general overview, it’s important to note that individual variations exist. Factors such as an individual’s metabolism, digestive health, and the specific composition of the food can influence digestion times. Here are some specific examples of food digestion times to give you a better understanding:
-
Watermelon: Due to its high water content, watermelon is quickly digested and typically leaves the stomach within 20 minutes.
-
Chicken Breast: Lean protein sources like chicken breast are usually digested within 1.5 to 2 hours.
-
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are packed with fiber and are generally digested within 30 to 40 minutes.
C. Factors Affecting Digestion Time for Different Foods
Several factors influence the digestion time of different foods. The presence of fiber, fat, and protein content in a meal can significantly impact how long it takes for the food to be fully digested. Fiber-rich foods, for instance, promote faster digestion due to their ability to add bulk and aid in smooth bowel movements. On the other hand, high-fat and high-protein foods can slow down digestion, as they require more time and effort to break down.
Moreover, individual factors such as age, overall health, and digestive disorders can affect digestion time. It’s essential to listen to your body and pay attention to any discomfort or irregularities in digestion. If you have specific concerns or experience persistent digestive issues, consulting a healthcare professional is always a wise decision.
Understanding the digestion times for different foods can help guide our dietary choices and promote a healthier digestive system. However, it’s important to remember that digestion is a complex process influenced by various factors. By being mindful of what we eat and how our bodies respond, we can make informed decisions to support optimal digestion and overall well-being.
Tips for Promoting Healthy Digestion
Maintaining a healthy digestive system is vital for overall well-being. By implementing a few simple practices into your daily routine, you can support optimal digestion and ensure your body efficiently processes the food you consume. Let’s explore some valuable tips that can promote a smooth and efficient digestion process.
A. Importance of a Balanced Diet and Regular Exercise
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting healthy digestion. Including a variety of nutrient-rich foods in your meals provides the necessary vitamins, minerals, and fibers that aid digestion. Opt for whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables to ensure a well-rounded diet that benefits your digestive system.
Regular exercise is also beneficial for digestion. Engaging in physical activity helps stimulate the muscles in your digestive tract, promoting the movement of food through your system. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, most days of the week to enhance your digestive health.
B. Incorporating Fiber-Rich Foods for Smooth Digestion
Fiber acts as nature’s broom, keeping your digestive system clean and running smoothly. Including fiber-rich foods in your diet can prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. Whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
To incorporate more fiber into your diet, start by gradually increasing your intake to allow your body to adjust. Additionally, ensure you stay well-hydrated, as fiber absorbs water and aids in maintaining healthy bowel movements.
C. Hydration and Its Impact on Digestion
Water is a vital component in the digestion process. It helps break down food, facilitates nutrient absorption, and aids in the smooth movement of waste through the intestines. Dehydration can lead to constipation and sluggish digestion, so it is essential to stay adequately hydrated.
Ensure you drink enough water throughout the day. While individual needs may vary, a general guideline is to aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily. Remember, other beverages such as herbal teas and fruit-infused water can contribute to your overall hydration as well.
By following these tips and making conscious choices in your diet and lifestyle, you can support a healthy digestive system and optimize the time it takes for your body to digest food. Let’s move forward and uncover more insights about digestion and the average digestion times for different foods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how long it takes to digest food is not only intriguing but also crucial for maintaining optimal health. The digestion process is a complex journey that involves various stages, enzymes, and organs working in harmony. Factors such as the type of food consumed, individual metabolism, and overall health can influence digestion time.
By being aware of these factors, we can make informed choices about our diet and lifestyle. Incorporating fiber-rich foods, staying hydrated, and maintaining a balanced diet can promote a smooth digestive system. Additionally, paying attention to our body’s cues and listening to any discomfort or irregularities can help us identify and address any potential digestive issues.
Remember, we are all unique individuals with varying digestion times. What works for one person may not work for another. It’s essential to listen to your body and make adjustments accordingly. If you have specific concerns or persistent digestive problems, it is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
So, the next time you sit down for a meal, take a moment to appreciate the intricate process that occurs within your body. Digestion is not just about the time it takes for food to be broken down and eliminated; it’s about nourishing your body with the nutrients it needs to thrive.
Stay curious, stay mindful, and embrace the journey of digestion as you embark on a path towards better digestive health. Cheers to a well-nourished body and a happy digestive system!
Note: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance regarding your specific health needs.